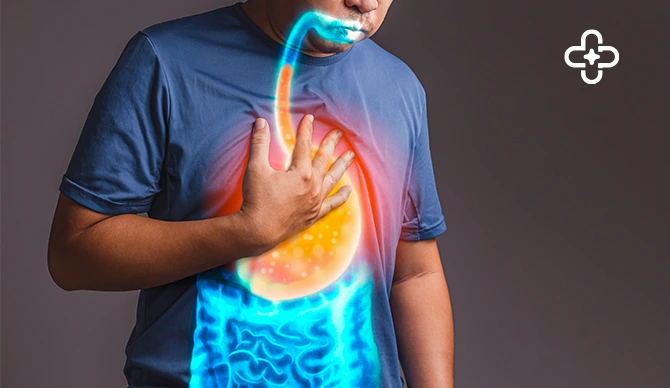
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive disorder characterized by frequent acid reflux, where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and potential complications. Many individuals dealing with GERD often wonder how long their symptoms will last. The duration of GERD depends on various factors, such as its severity, treatment approaches, and lifestyle adjustments.
Some people experience occasional acid reflux that resolves with minor adjustments, while others develop chronic GERD requiring long-term management. This article explores whether GERD can resolve on its own, how treatments affect its duration, and the risks of leaving it untreated.
What Is GERD?
GERD is a chronic condition where the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) becomes weak or relaxes inappropriately, allowing stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus. It differs from occasional heartburn, which is temporary and usually triggered by certain foods or lifestyle habits.
Short-Term vs. Chronic GERD
- Short-Term GERD: Some individuals experience GERD symptoms for a few days or weeks due to temporary factors such as dietary choices, stress, or infections. This form can often be managed through lifestyle modifications and over-the-counter antacids.
- Chronic GERD: GERD is classified as chronic if symptoms persist for several months or longer despite lifestyle modifications. Long-term GERD often requires medical intervention, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or surgery, to prevent complications.
Factors Affecting GERD Duration
- Stomach acid production: Higher acidity levels can prolong symptoms.
- Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) function: Weakness in this muscle leads to frequent reflux episodes.
- Dietary and lifestyle habits: Foods high in fat, caffeine, and acidity can trigger symptoms.
- Obesity and weight gain: Increased abdominal pressure can worsen GERD.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption: Both can relax the LES and increase acid production.
How Long Does GERD Last? Short-Term vs. Chronic GERD
Occasional GERD (Days to Weeks)
Some individuals may experience GERD symptoms for a short period due to temporary factors, such as:
- Eating spicy, fatty, or acidic foods
- Overeating
- Stress or anxiety
- Certain medications (e.g., NSAIDs, aspirin)
- Pregnancy-related hormonal changes
Short-term GERD can resolve within days or weeks with lifestyle modifications and avoidance of trigger foods.
Chronic GERD (Months to Years)
When GERD symptoms persist for months or years, it is considered a chronic condition. Factors that contribute to chronic GERD include:
- Untreated acid reflux episodes that lead to esophageal damage
- Dietary habits that continuously trigger reflux
- Inadequate lower esophageal sphincter function due to genetics, age, or lifestyle factors
- Hiatal hernia, where part of the stomach pushes into the chest, exacerbating reflux
Without intervention, chronic GERD can lead to serious complications such as esophageal strictures, Barrett’s esophagus, and an increased risk of esophageal cancer.
GERD Symptoms and Potential Complications
Common Symptoms
GERD presents a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild to severe. In addition to heartburn and chest pain, patients may also experience:
- Nausea
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Bloating
- Excessive burping
- Burning sensation
- Bitter or sour taste in the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chronic sore throat and hoarseness
- Coughing or worsening asthma symptoms
Serious Complications
If left untreated, GERD can lead to severe complications:
- Esophageal strictures: Narrowing of the esophagus due to scar tissue, making swallowing difficult.
- Barrett’s esophagus: Changes in the esophageal lining that increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
- Esophageal cancer: Chronic GERD is a risk factor for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus.
Diagnosing GERD
GERD diagnosis often involves:
- Esophageal manometry to evaluate LES function
- Endoscopy to assess esophageal damage
- pH monitoring to measure acid levels in the esophagus
- Biopsy (tissue sample) for esophageal changes
Additionally, routine annual wellness physical exams can help identify symptoms early and prevent complications by allowing healthcare providers to monitor overall digestive health.
How to Treat GERD and Manage Symptoms Effectively
Short-Term GERD Treatment
- Avoiding trigger foods (spicy, acidic, fatty foods)
- Eating smaller, frequent meals
- Elevating the head while sleeping
- Using over-the-counter antacids (Tums, Rolaids) or H2 blockers (Pepcid, Zantac)
Chronic GERD Management
Managing GERD effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment and lifestyle changes. At Manhattan Primary Care, we emphasize a holistic approach, integrating Preventive Care strategies to help patients reduce symptoms and avoid complications.
- Prescription Medications:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) like omeprazole, esomeprazole, and pantoprazole reduce stomach acid production.
- H2 receptor blockers like famotidine help decrease acid levels.
- Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding late-night meals
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake
- Surgical Options:
- Fundoplication: Strengthening the LES by wrapping the stomach around it.
- LINX device: A magnetic band around the LES to prevent reflux.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes to Prevent GERD Recurrence


Foods to Avoid
- Spicy foods
- Citrus fruits
- Carbonated beverages
- Chocolate and caffeine
- Fried and fatty foods
Lifestyle Modifications
A healthy weight plays a key role in managing GERD symptoms by reducing abdominal pressure and minimizing acid reflux. Our Weight management programs provide personalized guidance to help individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the severity of GERD episodes.
- Weight management: Reducing excess weight decreases abdominal pressure.
- Sleep position: Elevating the head of the bed helps prevent nighttime reflux.
- Avoid tight clothing: Reducing pressure on the abdomen minimizes reflux.
- Stress reduction: Meditation, exercise, and relaxation techniques help decrease symptoms.
When to See a Healthcare Professional for GERD
Signs That Require Medical Attention
If you’re experiencing persistent GERD symptoms despite lifestyle modifications, it’s crucial to seek medical help. At Manhattan Primary Care, our experienced healthcare professionals can evaluate your condition, recommend effective treatments, and help you prevent potential complications.
- Persistent acid reflux despite lifestyle changes
- Difficulty swallowing or choking sensations
- Unexplained weight loss
- Chronic sore throat or persistent cough
- Symptoms lasting more than a few weeks
Importance of Early Intervention
Seeking early medical advice can prevent complications such as Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal cancer. Individuals with persistent symptoms should consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
GERD duration varies depending on severity and treatment. While some individuals experience temporary acid reflux, chronic GERD can last for months or years without intervention. Effective management through lifestyle modifications, medication, and medical procedures is essential to prevent serious complications.
If you experience persistent GERD symptoms, consult a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan. Addressing GERD early is a critical component of chronic disease management and can improve quality of life while reducing the risk of long-term damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can stress and anxiety make GERD worse?
Yes, stress and anxiety can trigger behaviors that worsen GERD, such as overeating, smoking, and increased stomach acid production, leading to more frequent reflux episodes.
Is there a connection between GERD and sleep disorders?
Yes, GERD can cause nighttime reflux, leading to poor sleep quality, insomnia, and worsening sleep apnea. Elevating the head while sleeping and avoiding late-night meals can help.
Can GERD cause bad breath (halitosis)?
Yes, GERD can cause bad breath due to stomach acid and undigested food in the esophagus, creating an environment for bacteria growth. Proper oral hygiene and GERD treatment can help.
Are there any natural remedies that help relieve GERD symptoms?
Yes, natural remedies like aloe vera juice, ginger tea, and chewing sugar-free gum may help, but they should be used alongside medical treatments for best results.
Can GERD lead to nutritional deficiencies?
Yes, long-term GERD and medications like PPIs can reduce nutrient absorption, especially vitamin B12, magnesium, and calcium. Regular monitoring and a balanced diet can help prevent deficiencies.
Disclaimer
This blog is for informational & educational purposes only and does not intend to substitute any professional medical advice or consultation. For any health-related concerns, please consult with your physician, or call 911.